The choice of the right diamond grinding wheel must be determined according to the customer’s specific application. The decisive factor is the optimum interaction between wheel dimensions, grain size, bond and concentration.
Our employees with their many years of experience will be pleased to advise you by telephone or at your site regarding a high-quality and cost-effective design of a diamond grinding wheel for your process.

Applications
Diamond grinding wheels are used in a variety of applications. Below is a list of materials for which the use of diamond grinding wheels can be recommended:
- hard metal
- ceramics
- graphite
- glass
- Polycrystalline diamond and CBN plates
- Powder metallurgically prepared metal matrix composites (ferro-titanite)
- Hardmetal/steel combinations
- Quartz
- Ceramic materials of all kinds
- Ceramic magnetic materials
- Glass and carbon fibre reinforced plastics
- tungsten carbide
Bonds
The grinding behaviour of diamond grinding wheels is decisively influenced by the bond. The task of the bond is to optimally hold the abrasive grain at the grinding temperatures and grinding forces that occur and at the same time to create enough chip space for the removed material to be removed without any problems. Due to the large number of grinding problems that occur, a wide range of bonds is required:
- resin bonds
- metal bonds
- galvanic bonds
- ceramic bonds
Spectrum of bonds
Resin bonds
More than half of all grinding tasks can be accomplished with synthetic resin bonded diamond grinding wheels. The synthetic resin bond offers countless bond variations and very high stock removal rates.
| tie | cut | remark |
|---|---|---|
| K10R | dry / wet | Standard bond with medium hardness |
| K2010 | wet | Fine ground binding especially for polishing |
| K40X | wet | Very hard binding with a long service life |
| K20N | dry / wet | Wide pads with soft standard binding |
| KX30 | dry / wet | Very hard bond with long service life |
| K5020 | oil | Copper bonding cutter wet/oil |
| K7010 | oil | Hard copper bond wet/oil |
| K41X | oil | Copper bond Cutter CNC (11V9+12V9) DIA+CBN Oil |
| WTX1 | oil | Copper bond Cutter CNC (11V9+12V9) DIA+CBN Oil |
| WTX3 | oil | Copper bond Cutter CNC (11V9+12V9) DIA+CBN Oil |
| AK600 | dry | Dry ground bond with good stock removal rate |
Metal bonds
Metal bonds are characterised by very high grain retention forces. For the continuous self-sharpening of blunted diamond tips, large infeed forces are required which produce increased heat generation. Metal bonds should therefore always be used for wet grinding. Dry grinding is possible with small contact surfaces and low cutting depth. (Profile grinding on PETEWE, Studer, Hommel and Loewe).
Galvanic bonds
With electroplated nickel bonding, usually only one grain layer of diamond is held (2- or 3-layer is conditionally possible). The electroplated S-bond with diamond as abrasive is particularly suitable for processing less hard, but wearing materials such as graphite, mineral- or glass-fibre-reinforced plastics and the like.
Ceramic bonds
These bindings are characterized by porosity and profilability.
Concentration
The concentration determines the abrasive grain content (CBN) in the abrasive coating. The performance of CBN abrasive tools is determined significantly by the concentration. It influences the service life of the grinding tool, the profile retention, the stock removal rate and the grinding quality. This results in the following concentration gradations:
The basis for the concentration specification is the value C100, which corresponds exactly to 25% by volume of pure CBN in the abrasive coating.
For CBN this is the result:
C100 = 25 vol.% = 4.4 carat/cm3 (grinding wheel coating 1 kt = 0.2 g)
| Designation | Concentration | Percentage by volume |
|---|---|---|
| C25 | 1,10 ct/cm3 | 6,25 |
| C38 | 1,67 ct/cm3 | 9,50 |
| C50 | 2,20 ct/cm3 | 12,50 |
| C75 | 3,30 ct/cm3 | 18,75 |
| C100 | 4,40 ct/cm3 | 25,00 |
| C125 | 5,50 ct/cm3 | 31,25 |
The concentration determines the price on the one hand and the overall grinding behaviour of the disc on the other hand.
Picard tip:
- Higher concentrations (C100-C125-C150 / V240-V360) are appropriate when high profile retention, narrow covering widths, high bond hardness and deep grinding are required.
- Medium concentrations (C50-C75 / V120-V180) are recommended for cup wheels and peripheral wheels with larger lining widths and finer grain sizes.
- Low concentrations (C38-C50 / V120) are primarily used for very fine grain sizes.
Grain
The selection of CBN grain sizes is decisive for the stock removal rate and the resulting cutting results and surface qualities. The service life of the abrasive tool is also influenced by the abrasive grain size. Due to the large selection of synthetically produced abrasive grains in combination with the different bond types, the quality of the abrasive tool can be optimally adapted to your grinding operation.
For synthetic resin bonded abrasive tools, nickel coated abrasive grains are mainly used. Special coating processes enable adhesion possibilities in the bond, which also improve the thermal conductivity (see table of grit sizes below). In order to meet the various grinding requirements, there are a large number of grain sizes which have been combined into one standard by the FEPA (Fédération Européene des Fabricants de Produits Abrasifs).
The same grain sizes apply to diamond and CBN. Diamond grains are identified by a D (e.g. D126), CBN grains by a B (e.g. B126).
| Grain | Diamond | CBN |
|---|---|---|
| coarsely | D251 | B251 |
| D181 | B181 | |
| D151 | B151 | |
| medium | D126 | B126 |
| D107 | B107 | |
| D91 | B91 | |
| D76 | B76 | |
| D64 | B64 | |
| fine | D54 | B54 |
| D46 | B46 | |
| very fine | D15 | B15 |
| D7 | B7 | |
| D3 | B3 |
The grain size determines both the stock removal rate of CBN grinding wheels and the surface quality that can be achieved on the workpiece. The higher stock removal rate is generally achieved with coarser grit sizes. Finer grits improve the grinding quality, but at the same time reduce the stock removal rate.
Cutting speeds
The cutting speed of the CBN grinding tool has a very large influence on the service life, grinding performance and surface quality of the workpiece to be ground. The values listed below are guide values for setting the cutting speed:
| Resin bond | Diamond | CBN |
|---|---|---|
| dry grinding | 12 - 18 m/s | 16 - 22 m/s |
| wet grinding | 25 - 30 m/s | 25 - 30 m/s |
Forms
The selection of CBN grain sizes is decisive for the stock removal rate and the resulting cutting results and surface qualities. The service life of the abrasive tool is also influenced by the abrasive grain size. Due to the large selection of synthetically produced abrasive grains in combination with the different bond types, the quality of the abrasive tool can be optimally adapted to your grinding operation.
For synthetic resin bonded abrasive tools, nickel coated abrasive grains are mainly used. Special coating processes enable adhesion possibilities in the bond, which also improve the thermal conductivity (see table of grit sizes below). In order to meet the various grinding requirements, there are a large number of grain sizes which have been combined into one standard by the FEPA (Fédération Européene des Fabricants de Produits Abrasifs).
The same grain sizes apply to diamond and CBN. Diamond grains are identified by a D (e.g. D126), CBN grains by a B (e.g. B126).
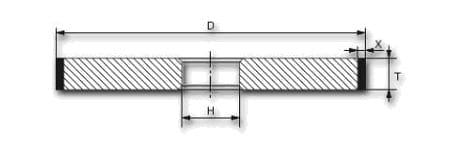
| shape | D | X | T | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 1 A1 | 100 | 4 | 6 | 20 | B126 | C75 | K20N |
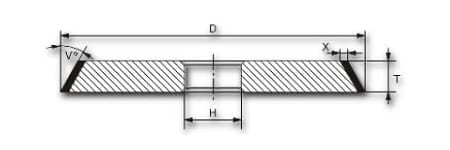
| shape | D | X | V | T | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 1 V1 | 100 | 3 | 60° | 12 | 20 | B91 | C100 | K7010 |
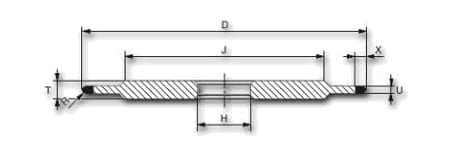
| shape | D | X | R | U | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 14 F1 | 100 | 2,5 | 2 | 4 | 32 | B91 | C100 | K20R |
| shape | V | D | U | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 14 EE1 | 60° | 125 | 4 | 4 | 20 | B64 | C75 | K20R |
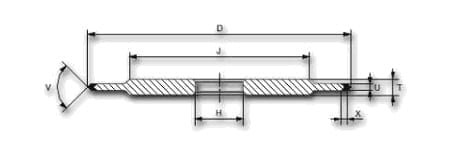
| shape | D | W | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 4 A2 | 125 | 5 | 2 | 20 | B91 | C75 | K20R |
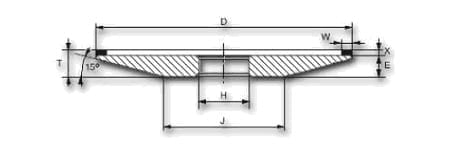
| shape | D | W | X | T | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 4 BT9 | 100 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 32 | B64 | C75 | K20R |
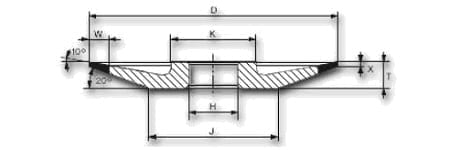
| shape | D | W | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 6A2 | 125 | 12,5 | 2 | 20 | B126 | C50 | K20R |
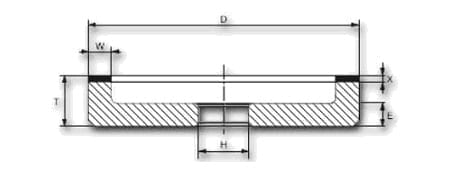
| shape | D | W | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 6A9 | 100 | 3 | 10 | 25 | B126 | C75 | K20R |
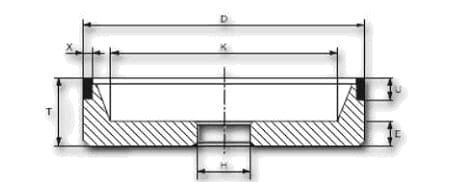
| shape | D | W | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 11A2 | 100 | 8 | 2 | 20 | B64 | C50 | K20R |
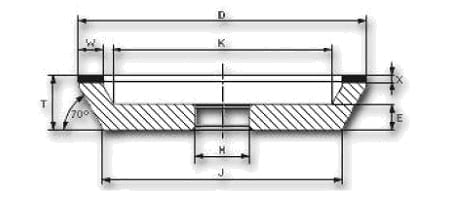
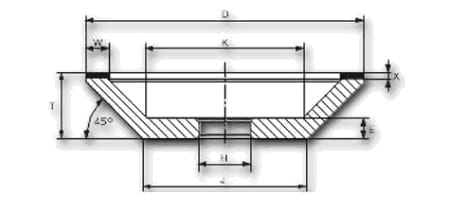
| shape | D | W | X | H | grain | concentration | tie |
| 12A2-45° | 100 | 10 | 4 | 20 | B64 | C50 | K20R |